Multi-modal Person Identification (MMPI) is a software technology for multi-modal recognition of persons according to their faces and the way they walk. The recognition process is based on analysis of detected face images and motion capture data — both acquired by motion capturing devices, including popular Microsoft Kinect and ASUS Xtion. The acquired data are firstly preprocessed by (1) detecting face images and extracting MPEG-7 face features and (2) detecting walk cycles and extracting movement features in form of relative velocities of the specific joints for each walk cycle. Both the face and walk-cycle features extracted from a query motion are used to retrieve two independent sets of the most similar faces and walk cycles. These retrieved sets are processed by a multi-modal classification method to recognize the query person identity. The MMPI technology is demonstrated via a ​web application that allows users to select a query motion and verify whether the technology recognizes the query person correctly.
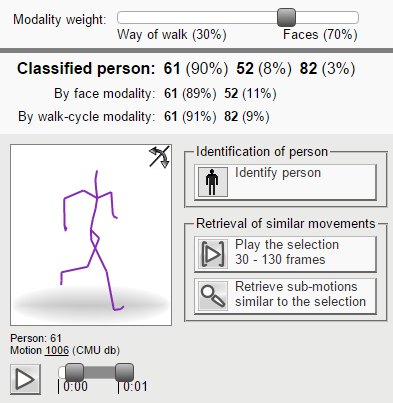
The demonstration application indexes 6,994 detected face images which are assigned to 2,515 motions (it corresponds to more than 12 hours of video data with about 5.4 million frames). Each motion represents a given kind of activity performed by a given actor. A single motion is represented by a sequence of poses that are drawn on the web-page canvas in form of human stick figures (each database motion has assigned a different color). The displayed stick figure is drawn for a current frame that can be changed by moving a range slider located under the canvas (the slider length corresponds to the motion length). Each motion can be processed to identify the actor identity by clicking the “Identify person” button. After clicking this button, face images and walk cycles are detected within the selected motion and used to retrieve two independent sets of the most similar faces and walk cycles within the database of indexed motions. The retrieved sets are finally classified based on the modality-weight slider to estimate the person identity, which is anonymized by its id.
Another advantage of MMPI is its ability to efficiently search for the most similar movements (sub-motions) within the indexed motions. This functionality allows users to specify a query sub-motion by setting its beginning and ending frame. After the query sub-motion selection and clicking the “Retrieve sub-motions similar to the selection” button, the technology is utilized to retrieve query-similar sub-motions which are then displayed on a web page and ordered from the left to right according to their similarity score. The number of the retrieved sub-motions is limited to the 50 most similar ones. A new query can also be defined by selecting a query motion from the retrieved results.
Related Publications
- J. Valcik, J. Sedmidubsky, P. Zezula: Assessing similarity models for human-motion retrieval applications. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. ISSN 1546-427X, 2015.
- J. Sedmidubsky, V. Mic, and P. Zezula: Face Image Retrieval Revisited. In 8th International Conference on Similarity Search and Applications (SISAP 2015). Springer-Verlag, 2015.
- J. Sedmidubsky, J. Valcik: Retrieving Similar Movements in Motion Capture Data. In 6th International Conference on Similarity Search and Applications (SISAP 2013). Springer-Verlag, 2013.
- J. Sedmidubsky, J. Valcik, P. Zezula: A Key-Pose Similarity Algorithm for Motion Data Retrieval. In 12th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems (ACIVS 2013). Springer-Verlag, 2013.
Open-source License
The MMPI technology is implemented in Java. The web application demonstrating functionality of this technology is implemented as a Java web application for Apache Tomcat. Both implementations are provided as open-source. The core of implementations can be downloaded here. For further information about the technology and web application can be acquired by contacting us at address: xsedmid [at] fi.muni.cz.
The MMPI technology is developed under the project Efficient Searching in Large Biometric Data (No. VG20122015073) within the security-research programme (BV II/2-VS) funded by Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic.