Current motion capturing technologies (e.g., Microsoft Kinect, Vicon Vantage, Asus Xtion…) record human motions at high frame-per-second rates. Motions are recorded as a series of 3D coordinates of body joints in space and time. The recorded motion data can be processed and utilized in a variety of applications, for example, in sports for comparing the performance of athletes, in security for identifying special-interest persons, in medicine for determining the success of rehabilitative treatments. All these applications require an effective and efficient (sub)motion-to-motion similarity matching.
DEMO #1: Action recognition
 Classification task: recognize labels of any user-selected short motion. A short motion (sub)sequence is selected as a query. Retrieval engine compares the query with 2K+ categorized motion samples to obtain the ranked list of nearest matches from which the most probable action label is obtained. The demonstration currently supports 130 label categories.
Classification task: recognize labels of any user-selected short motion. A short motion (sub)sequence is selected as a query. Retrieval engine compares the query with 2K+ categorized motion samples to obtain the ranked list of nearest matches from which the most probable action label is obtained. The demonstration currently supports 130 label categories.
»Try the action recognition demo
DEMO #2: Subsequence search
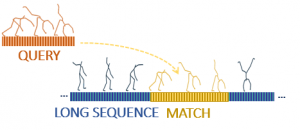 Subsequence search task: given a short query, search for similar subsequences within long motions. A total motion sequence of 12 hours can be searched. A short query motion is specified by the user using the query-by-example paradigm. Query-similar sub-motions are retrieved and displayed, and ordered according to their similarity score. A new query can be selected from the retrieved results.
Subsequence search task: given a short query, search for similar subsequences within long motions. A total motion sequence of 12 hours can be searched. A short query motion is specified by the user using the query-by-example paradigm. Query-similar sub-motions are retrieved and displayed, and ordered according to their similarity score. A new query can be selected from the retrieved results.
»Try the subseqeunce search demo
LSMB19: Dataset for benchmarking search and annotation
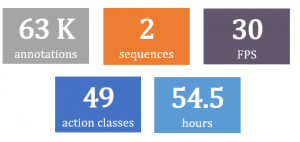 We propose a benchmark to evaluate search and annotation algorithms. The benchmark contains a motion dataset of 2 very long and continuous unsegmented 3D skeleton sequences, training and testing data for two modalities (cross-subject and cross view), 98 search queries and ground truth labels.
We propose a benchmark to evaluate search and annotation algorithms. The benchmark contains a motion dataset of 2 very long and continuous unsegmented 3D skeleton sequences, training and testing data for two modalities (cross-subject and cross view), 98 search queries and ground truth labels.
»Visit LSMB19 benchmark homepage
Related Publications
- J. Sedmidubsky, P. Elias, P. Budikova, P. Zezula: Content-Based Management of Human Motion Data: Survey and Challenges. IEEE Access. IEEE, 2021.
doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075766. - P. Budikova, J. Sedmidubsky, J. Horvath, P. Zezula: Towards Scalable Retrieval of Human Motion Episodes. In IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM). IEEE, 2020.
doi:10.1109/ISM50513.2020. - J. Sedmidubsky, P. Budikova, V. Dohnal, P. Zezula: Motion Words: A Text-like Representation of 3D Skeleton Sequences. In 42nd European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR). Cham: Springer, 2020.
doi:10.1007/978-3-030-45439-5_35. - J. Sedmidubsky, P. Elias, P. Zezula:Â Searching for Variable-Speed Motions in Long Sequences of Motion Capture Data. Information Systems, Elsevier, 2019.
doi:10.1016/j.is.2018.04.002. - F. Carrara, P. Elias, J. Sedmidubsky, P. Zezula: LSTM-Based Real-Time Action Detection and Prediction in Human Motion Streams. Multimedia Tools and Applications, Springer US, 2019.
doi:10.1007/s11042-019-07827-3. - J. Sedmidubsky, P. Elias, P. Zezula: Benchmarking Search and Annotation in Continuous Human Skeleton Sequences. In International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR 2019). New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2019.
doi:10.1145/3323873.3325013. - J. Sedmidubsky, P. Elias, P. Zezula:Â Effective and Efficient Similarity Searching in Motion Capture Data. Multimedia Tools and Applications, Springer US, 2018.
doi:10.1007/s11042-017-4859-7. - J. Valcik, J. Sedmidubsky, P. Zezula: Assessing similarity models for human-motion retrieval applications. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. ISSN 1546-427X, 2015.
doi: 10.1002/cav.1674. - J. Sedmidubsky, J. Valcik, P. Zezula: A Key-Pose Similarity Algorithm for Motion Data Retrieval. In 12th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems (ACIVS 2013). Springer-Verlag, 2013.
doi:Â 10.1007/978-3-319-02895-8_60.



